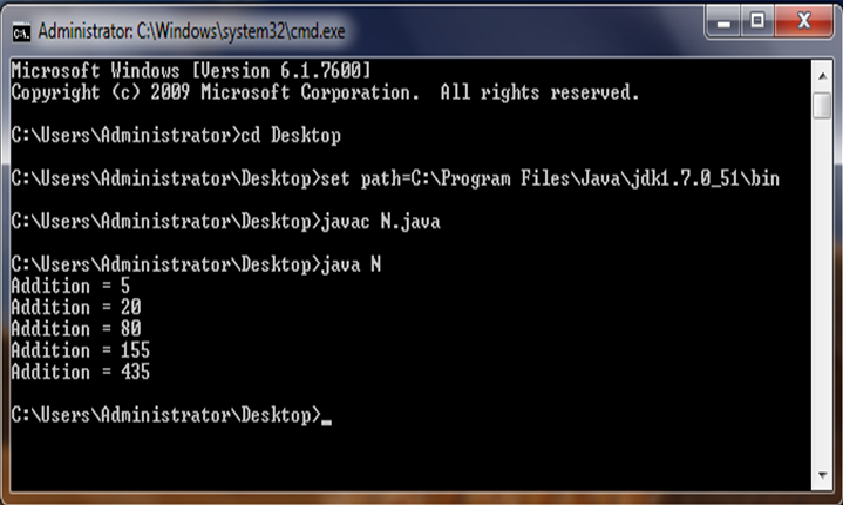
Problem Statement:
The Utopian tree goes through 2 cycles of growth every year. The first growth cycle occurs during the monsoon, when it doubles in height. The second growth cycle occurs during the summer, when its height increases by 1 meter.
Now, a new Utopian tree sapling is planted at the onset of the monsoon. Its height is 1 meter. Can you find the height of the tree after N growth cycles?
Input Format
The first line contains an integer, T, the number of test cases.
T lines follow. Each line contains an integer, N, that denotes the number of cycles for that test case.
Constraints
1 <= T <= 10
0 <= N <= 60
Output Format
For each test case, print the height of the Utopian tree after N cycles.
Sample Input #00:
Explanation #00:
There are 2 test cases. When N = 0, the height of the tree remains unchanged. When N = 1, the tree doubles its height as it's planted just before the onset of monsoon.
Sample Input: #01:
There are 2 testcases.
N = 3:
the height of the tree at the end of the 1st cycle = 2
the height of the tree at the end of the 2nd cycle = 3
the height of the tree at the end of the 3rd cycle = 6
N = 4:
the height of the tree at the end of the 4th cycle = 7
Now, a new Utopian tree sapling is planted at the onset of the monsoon. Its height is 1 meter. Can you find the height of the tree after N growth cycles?
Input Format
The first line contains an integer, T, the number of test cases.
T lines follow. Each line contains an integer, N, that denotes the number of cycles for that test case.
Constraints
1 <= T <= 10
0 <= N <= 60
Output Format
For each test case, print the height of the Utopian tree after N cycles.
Sample Input #00:
2
0
1
1
2
Explanation #00:
There are 2 test cases. When N = 0, the height of the tree remains unchanged. When N = 1, the tree doubles its height as it's planted just before the onset of monsoon.
Sample Input: #01:
2
3
4
6
7
There are 2 testcases.
N = 3:
the height of the tree at the end of the 1st cycle = 2
the height of the tree at the end of the 2nd cycle = 3
the height of the tree at the end of the 3rd cycle = 6
N = 4:
the height of the tree at the end of the 4th cycle = 7